 The Minneapolis-St. Paul metropolitan area is a national leader in finance, advanced manufacturing, agriculture and retailing.
The Minneapolis-St. Paul metropolitan area is a national leader in finance, advanced manufacturing, agriculture and retailing.
Medical devices, electronics and processed foods are strong suits recognized globally.
Want the freshest data delivered by email? Subscribe to our regional newsletters.
3/20/2023 9:00:00 AM
Tim O'Neill
March is Women's History Month, where the study, observance, and celebration of the vital role of women in American history is commemorated and encouraged. To a similar end, this month we'll study, observe, and celebrate the vital role of women in the Twin Cities Metro Area's labor market.
Using data from the U.S. Census Bureau's Quarterly Workforce Indicators (QWI) program, we can get an idea of how total employment has shifted from pre-COVID-19 levels by analyzing the change between the second quarters of 2019 and 2022. During that period, total jobs held by female workers in the Metro Area declined by 3.4%, compared to a 3.9% drop for men. This is equivalent to approximately 30,940 jobs lost for females. In other words, total female employment during the second quarter of 2022 was at 96.6% of its respective total employment during the second quarter of 2019, compared to 96.1% for males.
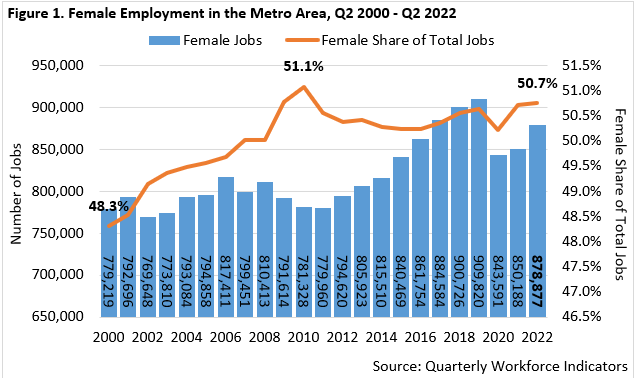
Between the second quarters of 2010 and 2019, total jobs held by female workers increased in the Metro Area by 16.4% (+128,490 jobs). Such employment then fell by 7.3% (-66,230 jobs) between the second quarters of 2019 and 2020. Female-held jobs then increased by 4.2% (+35,290 jobs) between the second quarters of 2020 and 2022 (Figure 1). Overall, female employment loss between 2019 and 2020 was more severe than male employment loss (-7.3% versus -5.7%) but has rebounded more rapidly between 2020 and 2022 (+4.2% versus +2.0%).
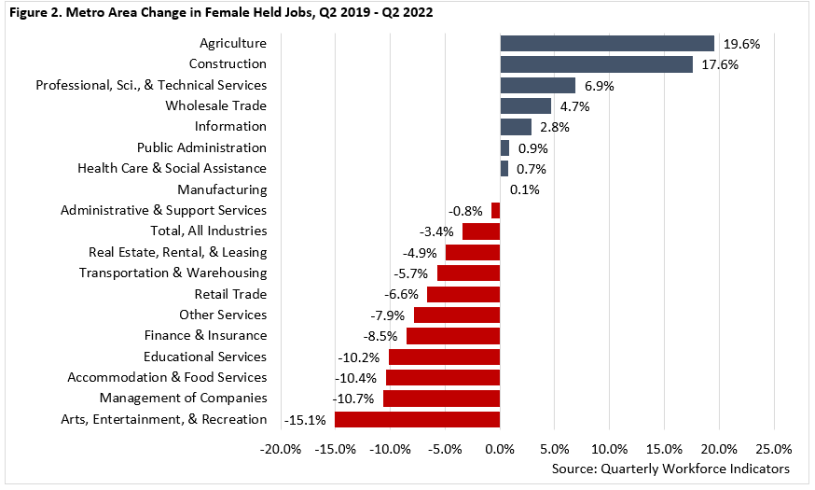
Exploring these trends by industry provides a more complete picture of the Metro Area's changing labor market by gender. The industries with the most significant losses in female-held jobs between the second quarters of 2019 and 2022 include:
Meanwhile, the industries with the most significant increases in female-held jobs between the second quarters of 2019 and 2022 include:
Last year, we looked at female employment in the Metro Area using DEED's Quarterly Employment Demographics (QED) tool. This data revealed those industries with higher shares of female employment in the Metro Area, including Health Care & Social Assistance, Educational Services, Other Services, Finance & Insurance, and Accommodation & Food Services. The industries with lower shares of female employment include Construction, Mining, Transportation & Warehousing, Manufacturing, Wholesale Trade, Information, and Administrative & Support Services.
Contact Tim O'Neill, Labor Market Analyst, at timothy.oneill@state.mn.us