by Amanda O'Connell
September 2023
What makes Southwest Minnesota's economy unique? According to DEED's Location Quotient Tool, Southwest Minnesota has a higher concentration of employment in Agriculture, Manufacturing, Public Administration, Educational Services, Retail Trade, and Utilities than the state.
Location Quotients (LQ) are a measurement of an industry's employment concentration in a specified geography relative to that industry's concentration in a larger benchmark region. An LQ of 1.0 signifies that the local area's employment concentration mirrors that of the larger benchmark area. When the LQ surpasses 1.0, it indicates a heightened employment concentration, while an LQ below 1.0 suggests a comparatively lower employment concentration within the smaller area.
Southwest Minnesota boasts an array of industries that play a crucial role in shaping the local economy and communities. This article aims to provide comprehensive insights into the distinct industries that thrive in Southwest Minnesota.
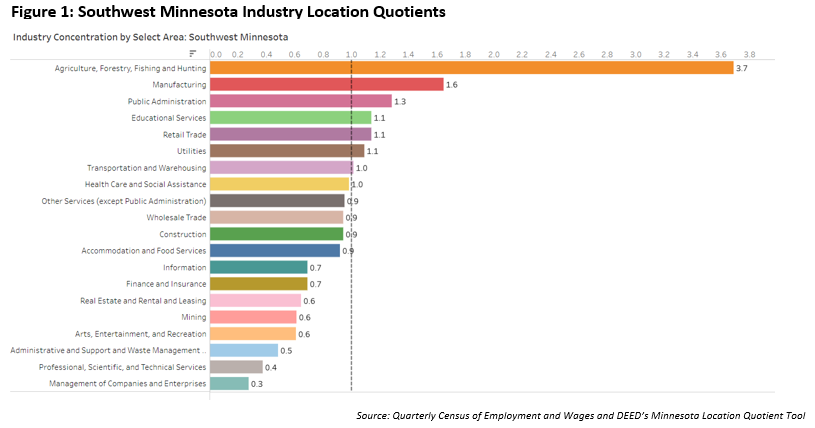
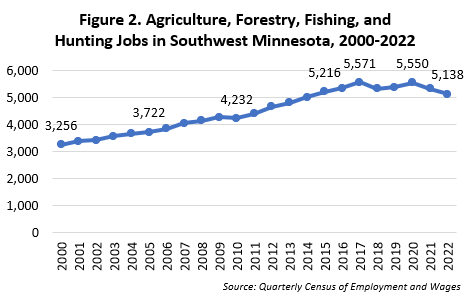 At 3.7, Southwest Minnesota has the highest location quotient of the six planning regions in the state for Agriculture, Forestry, Fishing, and Hunting. In 2022 this region boasted an average of 720 firms that provided 5,138 jobs, offering an average annual wage of $49,907. Over the years Southwest Minnesota has experienced substantial job growth in this industry, adding 1,882 jobs since 2000, a remarkable 57.8% increase. The peak employment levels were recorded in 2017, with 5,571 jobs, followed by a slight dip in 2018 and 2019, then job gains in 2020, before further settling in 2021 and 2022.
At 3.7, Southwest Minnesota has the highest location quotient of the six planning regions in the state for Agriculture, Forestry, Fishing, and Hunting. In 2022 this region boasted an average of 720 firms that provided 5,138 jobs, offering an average annual wage of $49,907. Over the years Southwest Minnesota has experienced substantial job growth in this industry, adding 1,882 jobs since 2000, a remarkable 57.8% increase. The peak employment levels were recorded in 2017, with 5,571 jobs, followed by a slight dip in 2018 and 2019, then job gains in 2020, before further settling in 2021 and 2022.
Animal Production and Aquaculture is the largest subsector, with 3,639 jobs across 325 firms. Crop Production is next largest with 852 jobs distributed among 254 firms, followed by Support Activities for Agriculture and Forestry with 596 jobs at 124 firms, Forestry and Logging with 33 jobs at 12 firms, and Fishing, Hunting, and Trapping with 17 jobs found in six firms. Among these subsectors Forestry and Logging offer the highest annual wage at $60,424, followed by Animal Production and Aquaculture at $51,584, and Support Activities for Agriculture and Forestry at $49,192.
Looking at specific counties within Southwest Minnesota, Sibley County boasts the highest LQ at an impressive 22, meaning Agriculture employment is more than 20 times more concentrated in Sibley County than the state as a whole. In 2022 Sibley County had an average of 705 jobs at 34 firms within the Agriculture, Forestry, Fishing, and Hunting industry. The second highest LQ was observed in Lincoln County, standing at 10.1, with 128 jobs among 15 firms. Martin County followed with an LQ of 6.6, featuring 440 jobs supported by 65 firms.
With a location quotient of 1.6, Southwest Minnesota also had the highest LQ of the six planning regions in the state for Manufacturing. Central and Southeast were tied for second with an LQ of 1.3. In 2022 the Manufacturing industry had 633 establishments providing 32,097 jobs with an average annual wage of $61,880 in Southwest Minnesota.
The top four subsectors in the region include Food Manufacturing (12,022 jobs at 121 firms), Machinery Manufacturing (3,574 jobs at 66 firms), Printing and Related Support Activities (2,381 jobs at 62 firms), and Fabricated Metal Product Manufacturing (2,124 jobs with 95 firms). These four subsectors make up almost two-thirds (62.6%) of all Manufacturing jobs in Southwest Minnesota.
Nobles County had the highest LQ of the 23 counties in Southwest Minnesota at 2.9, meaning Manufacturing employment was three times as concentrated in Nobles as the state. In 2022 Nobles County had 33 firms providing 3,381 jobs, accounting for 32.9% of the total employment in the county. Similarly, Jackson County had an LQ of 2.8 with 18 firms providing 1,551 jobs, which contributed 32.1% of the county's total employment.
In DEED's latest Job Vacancy Survey for Quarter 2 of 2022, the Manufacturing industry emerged as the second-largest contributor to job vacancies in the region, totaling 3,062 job vacancies as employers struggled to find workers to fill their open positions. Notably, just 16% of these job vacancies required post-secondary education or training, indicating that a majority of job opportunities within this industry may be accessible to individuals without higher education. Additionally, 30% of these job vacancies were classified as part-time positions, providing flexibility in employment options for individuals seeking work in Manufacturing.
When we examine the wage offers made within the Manufacturing sector, the survey revealed a median hourly wage offer of $17.46. This figure stands out as almost $1.00 higher than the median hourly wage offer observed across all industries in Southwest Minnesota. This wage differential suggests that Manufacturing jobs in the region offer competitive compensation, potentially making them attractive options for job seekers.
With a location quotient of 1.3 in Public Administration, Southwest Minnesota tied for second place with Northwest for the highest LQ of the six planning regions. Northeast Minnesota has the highest LQ at 1.6. In 2022 the Public Administration industry had 587 firms and 9,958 employees in Southwest Minnesota, providing average annual wages of $51,220. Public Administration contributes to 5.8% of total employment in Southwest Minnesota.
The largest subsectors in Public Administration include Executive, Legislative, and Other Government Support, with 300 establishments providing 6,722 jobs, followed by Administration of Human Resource Programs (1,362 jobs with 53 firms), Justice, Public Order, and Safety Activities (960 jobs with 64 firms), and Administration of Environmental Quality Programs (441 jobs and 69 firms). Government employment declined in 2020 with the outbreak of COVID-19 and stayed lower in 2021 before regaining about half the jobs lost from 2019 to 2020 in 2022.
 With a location quotient of 1.1, Southwest Minnesota has the second highest location quotient of the six planning regions in the state in Educational Services, following Northwest Minnesota (1.3). Educational Services provided 15,495 jobs with 236 firms in Southwest Minnesota in 2022, accounting for 9% of total employment in the region. Elementary and Secondary Schools was the largest subsector providing 11,627 jobs at 159 establishments. The second largest subsector was Colleges, Universities, and Professional Schools, which provided 2,865 jobs at 12 institutions in the region. Finally, Junior Colleges/Community Colleges were the third largest subsector with 466 jobs and 7 campuses.
With a location quotient of 1.1, Southwest Minnesota has the second highest location quotient of the six planning regions in the state in Educational Services, following Northwest Minnesota (1.3). Educational Services provided 15,495 jobs with 236 firms in Southwest Minnesota in 2022, accounting for 9% of total employment in the region. Elementary and Secondary Schools was the largest subsector providing 11,627 jobs at 159 establishments. The second largest subsector was Colleges, Universities, and Professional Schools, which provided 2,865 jobs at 12 institutions in the region. Finally, Junior Colleges/Community Colleges were the third largest subsector with 466 jobs and 7 campuses.
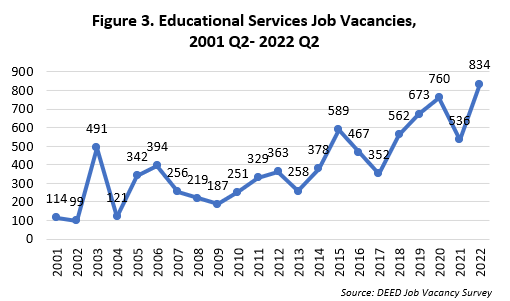
Southwest Minnesota is projected to increase employment in the Educational Services industry by 4.6% or 710 new jobs from 2020 to 2030. After declining during the pandemic, Elementary and Secondary Schools are expected to have the largest numeric increase of 596 jobs, a 5% increase, followed by Other Schools and Instruction with an increase of 52 jobs. Likewise, the region is currently experiencing a surge in job vacancies within the Educational Services industry, with a record high 834 job vacancies in 2022 (Figure 3). This indicates strong demand for educators, administrators, and support staff, underlining the need for a skilled and dedicated workforce to meet the educational needs of Southwest Minnesota's communities.
 The Retail Trade industry provided 19,308 jobs at 1,437 firms, with an average annual wage of $30,836 in Southwest Minnesota in 2022. Southwest and Southeast Minnesota both have an LQ of 1.1, which follows Central, Northwest, and Northeast Minnesota, which are all at 1.3.
The Retail Trade industry provided 19,308 jobs at 1,437 firms, with an average annual wage of $30,836 in Southwest Minnesota in 2022. Southwest and Southeast Minnesota both have an LQ of 1.1, which follows Central, Northwest, and Northeast Minnesota, which are all at 1.3.
Retail Trade encompasses 11.2% of total employment in Southwest Minnesota. There are three main subsectors of Retail Trade: Food and Beverage Stores has the most jobs, sitting at 4,312 jobs with 177 firms, followed by Motor Vehicle and Part Dealers with 2,538 jobs and 212 firms, and Building Material and Garden Equipment Supplies and Dealers with 1,773 jobs and 173 firms.
According to the most recent Job Vacancy Survey in 2022, the Retail Trade industry stood out with 1,851 job vacancies, ranking third highest among the 20 industries in the region. What's particularly noteworthy is that 77% of these job vacancies were for part-time positions. Even more striking, less than 5% of these positions required post-secondary education, and only 15% required one or more years of prior experience. These findings suggest Retail Trade jobs are particularly suitable for individuals looking for an entry level position, a position for their retirement, or who have an unfinished education and limited work experience.
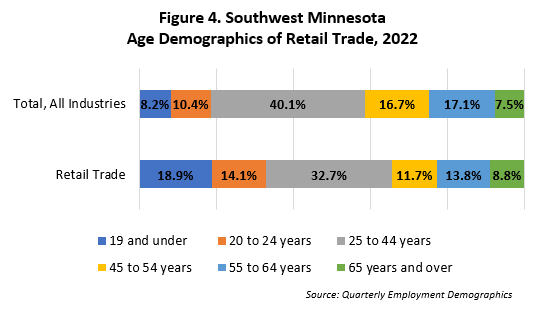
As depicted in Figure 4, the demographics of Retail Trade employment in Southwest Minnesota also paint an interesting picture. A substantial portion of Retail Trade jobholders in this region are either younger or older compared to the workforce across all industries. Specifically, individuals aged 19 and younger and those between the ages of 20 to 24 collectively constitute 33% of the Retail Trade workforce in Southwest, a stark contrast to the 18.6% they represent across all industries. Conversely, people aged 65 and over compromise 8.8% of Retail Trade employees, slightly surpassing the 7.5% representation observed across all industries.
The Utilities industry in Southwest Minnesota has a slightly above average LQ of 1.1. There are 900 jobs in the Utilities industry with 77 firms providing a high average annual wage of $99,736. Southwest Minnesota has the second lowest LQ for the Utilities industry of the six planning regions. Northeast Minnesota has the highest LQ of 2.3, followed by Central (1.6), then Northwest and Southeast (1.2).
Electric Power Generation, Transmission, and Distribution is the largest subsector with 762 jobs and 50 firms providing an average annual wage of $103,844, followed by Natural Gas Distribution with 76 jobs and nine firms, and Water, Sewage, and Other Systems with 61 jobs with 18 firms.
Southwest Minnesota's economic landscape is undeniably unique, characterized by a diverse range of industries that make a significant impact on both the local economy and the communities they serve. The region's high Location Quotients in Agriculture, Manufacturing, Public Administration, Educational Services, Retail Trade, and Utilities underscore the specialization and strength of these sectors within the region. These insights into Southwest Minnesota's economy can guide both job seekers and policymakers, showcasing the distinct opportunities that shape the region as it grows and changes.