by Mark Schultz and Tim O'Neill
May 2020
While recent events surrounding the Coronavirus have put a halt to many Personal Care and Laundry Services, such as hair care appointments and funerals, establishments are starting to open up, and businesses are beginning to operate again with some restrictions.
Personal and Laundry Services is a sub-sector of the Other Services (except Public Administration) sector. Most recent estimates show that the state has almost 28,700 Personal Care and Laundry Service jobs in 3,742 establishments, making up 1 percent of all jobs in the state. The largest portion of jobs under Personal Care and Laundry Services fall under personal care services, such as barber shops, hair salons, and diet and weight reducing centers. In all, Personal Care Services makes up 56.9 percent of the total jobs in Personal Care and Laundry Services. Also included under Personal Care and Laundry Services are death care services such as funeral homes and cemeteries, drycleaning and laundry services such as coin-operated laundries and dry cleaners, and other personal services such as pet care and parking lots and garages (see Table 1).
Table 1. Personal and Laundry Services Industry Employment Statistics (2019)
| Industry Title | Average Jobs | Average Establishments | Total Payroll | Average Annual Wage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total, All Industries | 2,900,290 | 178,242 | $172,936,995,226 | $59,644 |
| Other Services (except Public Administration) | 91,309 | 17,282 | $3,243,791,156 | $35,516 |
| Personal and Laundry Services | 28,679 | 3,742 | $841,408,130 | $29,328 |
| Personal Care Services | 16,325 | 2,391 | $455,511,945 | $27,872 |
| Death Care Services | 2,109 | 345 | $78,230,618 | $37,076 |
| Drycleaning and Laundry Services | 4,482 | 341 | $166,229,272 | $37,076 |
| Other Personal Services | 5,763 | 665 | $141,436,295 | $24,492 |
| Source: DEED Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages | ||||
Also shown in Table 1, annual wage estimates for this industry rest at $29,328 and are 50.8 percent lower than wages across all industries. This is likely because more jobs in the Personal and Laundry Services industry are part-time. As of 2018, according to the American Community Survey, 59.2 percent of those employed in Minnesota In Other Services reported working full-time and year-round compared to 68.1 percent who reported working full-time and year-round in all jobs in Minnesota. Overall, the average annual wages for this sub-sector increased by 24.8 percent over the last 10 years, resulting in a hike of $5,824. The largest annual wages were seen in death care services as well as dry cleaning and laundry services.
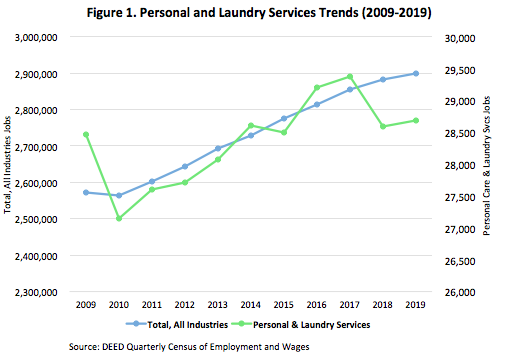
The number of jobs across all industries and in Personal and Laundry Services increased over the last decade. However, Personal and Laundry Services saw some ups and downs along the way. Overall, from 2009 to 2019 the Personal and Laundry Services industry gained only 219 jobs, growth of only 0.8 percent (see Figure 1).
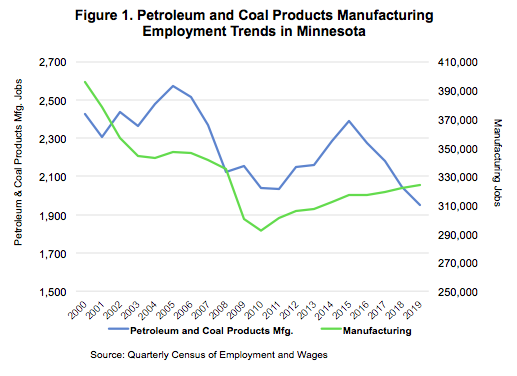
Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing is a small but high-paying industry sector within the State of Minnesota. As of annual 2019, there were 20 Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing establishments in Minnesota, supplying 1,950 jobs. Total payroll for this manufacturing sector topped $256.2 million that year. Where Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing accounted for 0.6 percent of the state's total manufacturing employment, it accounted for 1.2 percent of manufacturing's total payroll in the state. Accounting for a significantly higher share of Minnesota's total manufacturing payroll versus total manufacturing employment, it follows that average annual wages within Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing are high. At $131,508 average annual wages within Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing are 93.2 percent and 120.5 percent higher than the average annual wages for all manufacturing jobs and total employment in the state, respectively.
Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing is also highly concentrated within the State of Minnesota. While three of this sector's 20 establishments are in Northwest Minnesota, the remaining 17 are located in the Twin Cities Metro Area. Further, about 99 percent of the state's total employment in Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing is in the Metro Area.
Of Minnesota's 1,950 Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing jobs, 1,378 (70.7 percent) are designated within the Petroleum Refineries subsector. According to the North American Industrial Classification System (NAICS), this subsector comprises establishments primarily engaged in refining crude petroleum into refined petroleum. Interestingly, Minnesota does not have any crude oil reserves or production. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, however, three-tenths of all U.S. crude oil imports enter through Minnesota. Some of this crude oil, that enters either from Canada or North Dakota, is processed at refineries in Minnesota. Minnesota has the largest oil refinery in any of the non-oil-producing states. The refineries in Minnesota produce everything from transportation fuels and distillates to asphalt, propane, and more.
Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing in Minnesota hit a peak of 2,573 jobs in 2005. Over the next five years, between 2005 and 2010, the industry would lose 532 jobs, declining by 20.7 percent. Between 2010 and 2015, employment rebounded by 17.0 percent or 347 jobs. Since 2015, however, the industry shed a further 438 jobs, declining by 18.3 percent. Overall, between 2010 and 2019 employment in Petroleum and Coal Products Manufacturing declined by a slight 4.5 percent or 91 jobs (see Figure 1). For reference, total manufacturing employment during this time increased by 10.9 percent. Total employment across all industries increased by 13.1 percent between 2010 and 2019.
Planning on planting a tree or installing a fence? With tens of thousands of miles of pipeline throughout Minnesota, it's vital that you call before you dig! The national call-before-you-dig phone number is 811.
According to the North American Industry Classification System, or NAICS, "Industries in the Pipeline Transportation subsector use transmission pipelines to transport products, such as crude oil, natural gas, refined petroleum products, and slurry." Knowing this, it's easy to understand how vital this industry is in the State of Minnesota, as these transported products are used for daily commuting and traveling, heating, cooking and cleaning, and in the manufacturing of countless products. Pipelines within Minnesota include both long-distance transmission lines, as well as local distribution lines, which deliver energy products to businesses and households.
As of annual 2019, Minnesota had more than 68,000 miles of pipeline, which transported natural gas, anhydrous ammonia, crude oil, and refined petroleum products such as gasoline and diesel fuel.1 Local distribution and service lines account for the highest share of these miles. For example, of the nearly 64,800 miles of gas pipeline in Minnesota, over 59,200 miles (91.5 percent) were distribution lines. About 5,500 miles (8.5 percent) were long-distance transmission lines.2 Additionally, Minnesota has nearly 2,600 miles of pipeline for crude oil, nearly 600 miles of pipeline for hazardous liquids (such as propane and anhydrous ammonia), and over 1,800 miles of pipeline for refined petroleum products such as gasoline and diesel fuel. As a division of the Minnesota Department of Public Safety, the Minnesota Office of Pipeline Safety (MNOPS) is responsible for pipeline safety and underground utility damage prevention throughout the state.
While there are tens of thousands of miles of pipeline throughout the State of Minnesota, employment within this industry is relatively small. As of annual 2019, there were 74 Pipeline Transportation establishments supplying 678 jobs. Data from DEED's Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW) allows us to break this employment down by Pipeline Transportation of Oil, Pipeline Transportation of Natural Gas, and Other Pipeline Transportation which essentially covers refined petroleum products like gasoline and diesel fuel (see Table 1).
Table 1. Minnesota Pipeline Transportation Employment, 2019
| Industry | Number of Firms | Number of Jobs | Total Payroll ($1,000s) | Average Annual Wage | Job Change 2014 – 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total, All Industries | 178,242 | 2,900,290 | $172,936,995 | $59,644 | 170,677 (6.3%) |
| Pipeline Transportation | 74 | 678 | $81,052 | $119,236 | 59 (9.5%) |
| Pipeline Transportation of Crude Oil | 28 | 301 | $40,134 | $132,340 | 22 (7.9%) |
| Pipeline Transportation of Natural Gas | 26 | 222 | $22,779 | $102,440 | 24 (12.1%) |
| Other Pipeline Transportation | 20 | 154 | $18,139 | $117,520 | 12 (8.5%) |
| Source: DEED Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages | |||||
1Office of Pipeline Safety 2019 Annual Report . Minnesota Department of Public Safety.
2Minnesota Pipeline Profile: Mileage and Facilities, U.S. Department of Transportation.
As of annual 2019, the State of Minnesota had 373 Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing establishments supplying just over 16,900 jobs. Total payroll approached $1 billion, with average annual wages of $57,356. Of 21 specific manufacturing sectors, Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing was the state's seventh largest Manufacturing employing sector, with more jobs in the state than sectors such as Chemical Manufacturing, Wood Manufacturing, and Transportation Equipment Manufacturing. Overall, Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing makes up approximately 5 percent of the state's 323,918 manufacturing jobs (see Table 1).
Establishments within Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing produce goods by processing, you guessed it, plastics materials and raw rubber. The manufacturing of plastic and rubber products are combined into one industry as plastics are increasingly being used as a substitute for rubber. In the North American Industry Classification System (NAICS), products combined of multiple materials may be classified in distinct sectors. For example, some furniture includes plastics or rubber, but would be classified in Furniture Manufacturing. Table 1 lists those subsectors found in Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing. Examples of final products from these subsectors include plumbing fixtures, hardware, siding, trash containers, bottles, tires, and hoses - all, of course, comprised of plastics or rubber.
Table 1. Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing Employment in Minnesota, 2019
| NAICS Code | Industry | Number of Establishments | Number of Jobs | Total Payroll ($1,000s) | Avg. Annual Wage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Total, All Industries | 178,242 | 2,900,290 | $172,936,995 | $59,644 |
| 31 | Manufacturing | 8,269 | 323,918 | $22,052,647 | $68,068 |
| 326 | Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing | 373 | 16,909 | $969,821 | $57,356 |
| 3261 | Plastics Product Manufacturing | 317 | 15,084 | $863,275 | $57,200 |
| 32619 | Other Plastics Product Manufacturing | 235 | 10,483 | $590,357 | $56,316 |
| 32611 | Plastics Packaging Materials and Unlaminated Film and Sheet Manufacturing | 29 | 2,117 | $122,550 | $57,876 |
| 32612 | Plastics Pipe, Pipe Fitting, and Unlaminated Profile Shape Manufacturing | 26 | 1,710 | $113,925 | $66,612 |
| 32615 | Urethane and Other Foam Product (except Polystyrene) Manufacturing | 14 | 416 | $19,536 | $47,008 |
| 32614 | Polystyrene Foam Product Manufacturing | 6 | 161 | $7,928 | $49,296 |
| 32613 | Laminated Plastics Plate, Sheet (except Packaging), and Shape Manufacturing | 3 | 103 | $4,916 | $47,528 |
| 32616 | Plastics Bottle Manufacturing | 4 | 94 | $4,064 | $43,472 |
| 3262 | Rubber Product Manufacturing | 56 | 1,825 | $106,546 | $58,396 |
| 32629 | Other Rubber Product Manufacturing | 46 | 1,702 | $99,416 | $58,396 |
| 32621 | Tire Manufacturing | 6 | 116 | $6,726 | $58,240 |
| 32622 | Rubber and Plastics Hoses and Belting Manufacturing | 4 | 6 | $404 | $67,288 |
| Source: MN DEED Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW) | |||||
While three of five Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing jobs are in the Metro, a much higher share of such jobs are located in Central Minnesota. Central Minnesota accounts for about 10 percent of Minnesota's total employment, but 18 percent of the state's Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing Employment (see Table 2).
Table 2. Plastics and Rubber Products Manufacturing by Region in Minnesota, 2019
| Area | Total Jobs | Manufacturing Jobs | Plastics and Rubber Product Manufacturing Jobs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minnesota | 2,900,290 (100.0%) | 323,918 (100.0%) | 16,909 (100.0%) |
| Metro Area | 1,773,078 (61.1%) | 173,042 (53.4%) | 10,156 (60.0%) |
| Central MN | 278,111 (9.6%) | 41,961 (13.0%) | 3,052 (18.0%) |
| Southeast MN | 246,544 (8.5%) | 38,730 (12.0%) | 1,377 (8.1%) |
| Southwest MN | 176,514 (6.1%) | 31,338 (9.7%) | 1,014 (6.0%) |
| Northwest MN | 223,144 (7.7%) | 29,473 (9.1%) | 922 (5.5%) |
| Northeast MN | 143,487 (4.9%) | 8,899 (2.7%) | 353 (2.1%) |
| Source: MN DEED Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW) | |||